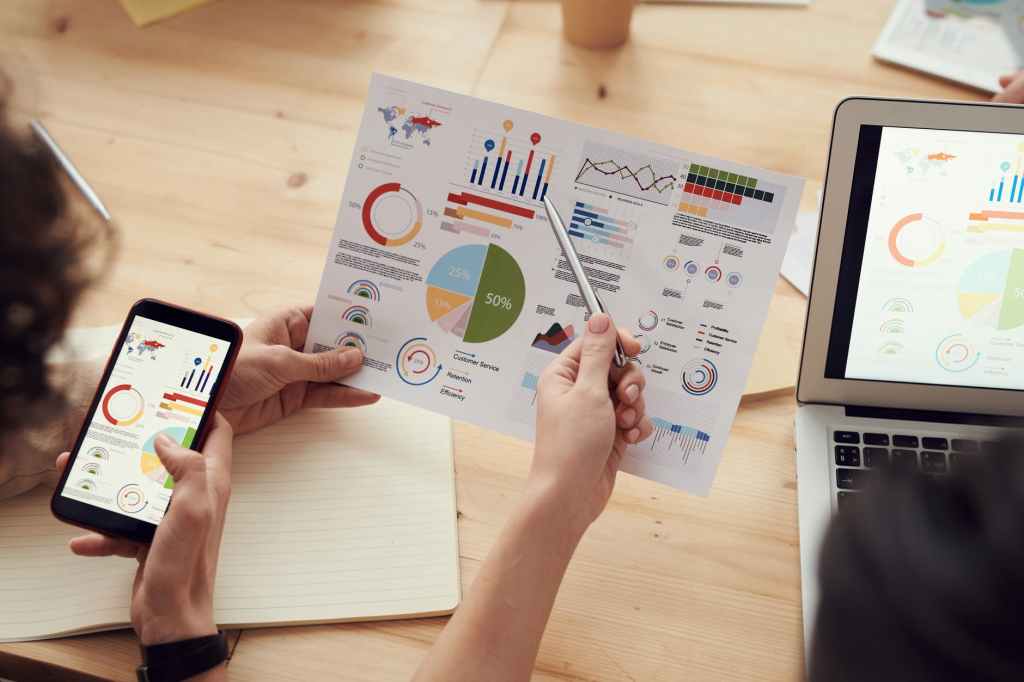
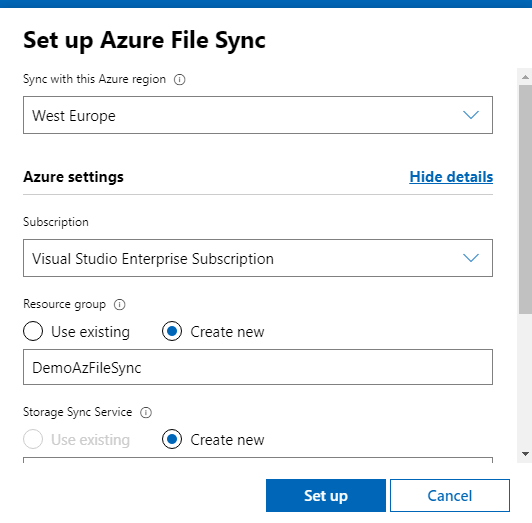
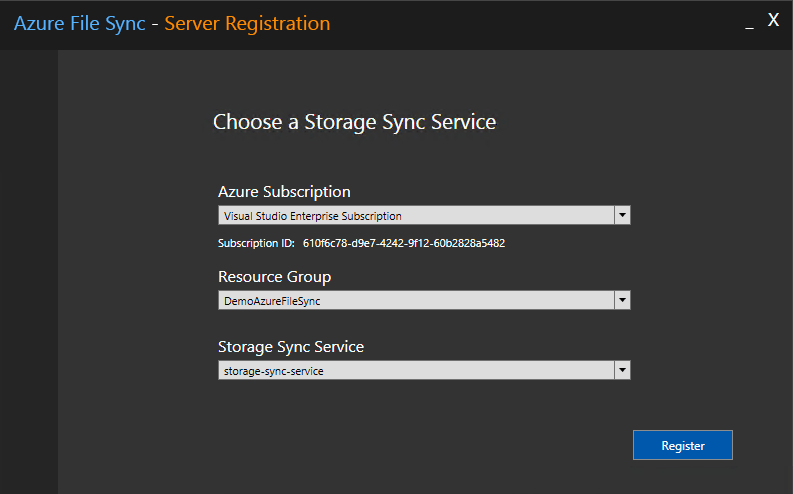
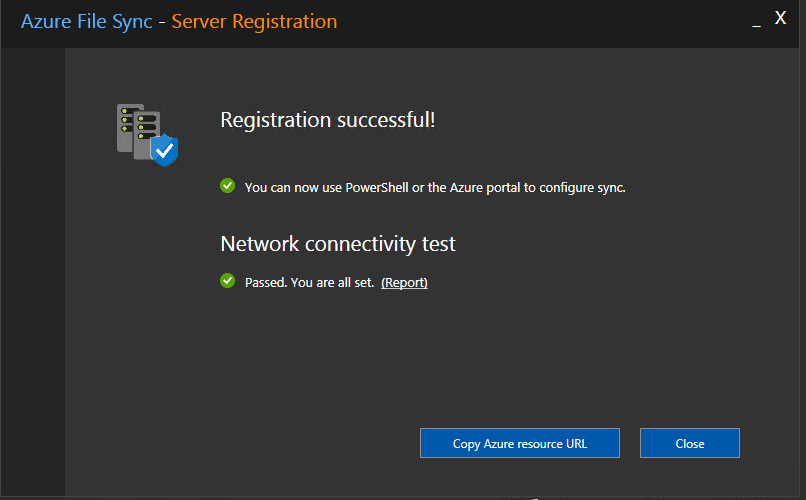
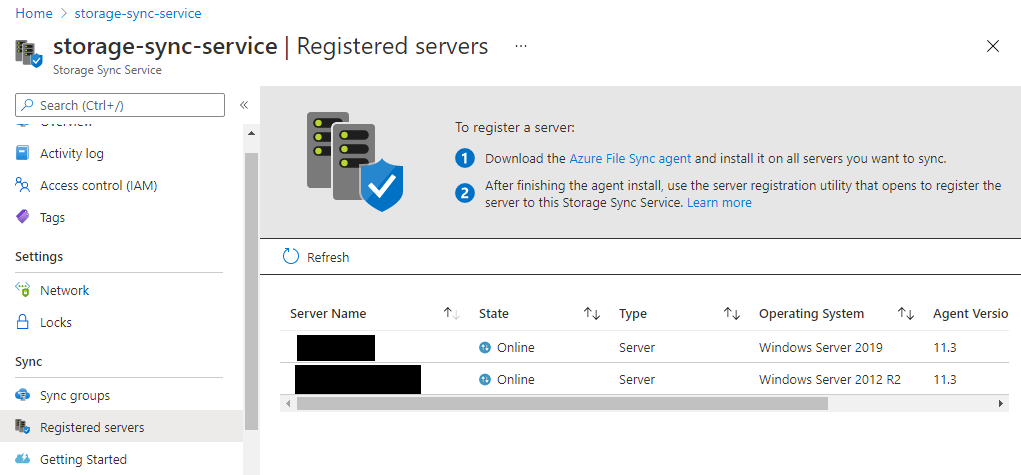
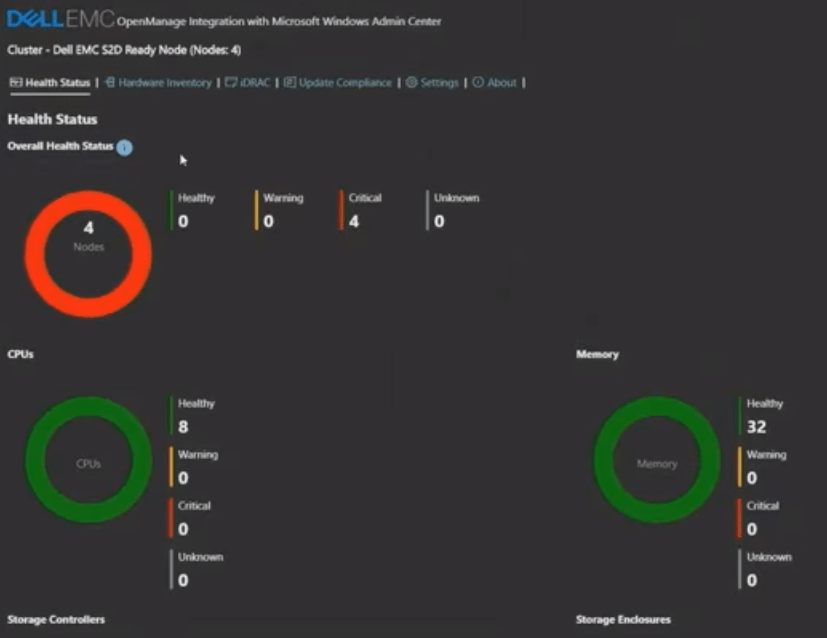
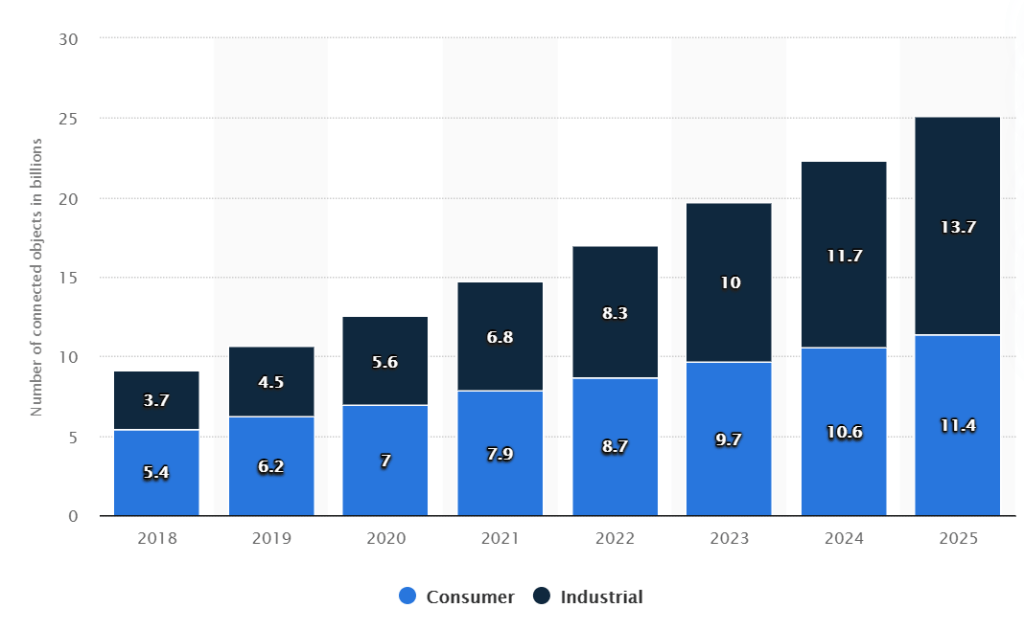
CNFC (Cloud Native Computing Foundation) can´t be more clear on their 2020 survey report:
The use of containers in production has increased to 92%, up from 84% last year, and up 300% from our first survey in 2016. Moreover, Kubernetes use in production has increased to 83%, up from 78% last year.
Related to the usage of cloud native tools there are also some clear tendences:
• 82% of respondents use CI/CD pipelines in production.
• 30% of respondents use serverless technologies in production.
• 27% of respondents use a service mesh in production, a 50% increase over last year.
• 55% of respondents use stateful applications in containers in production.
What happens when someone adopts containers just for testing in their company?…in less than 2 years the containers are adopted in pre-production and production as well.
Why containerization is so extended?
Here are some facts i figure out.
Devops friendly – Well, there are some reasons, clear as water .. Almost all the big companies within the enterprise segment have a devops CI/CD strategy already deployed..so they´ve realised that integrating the builds and delivery versions with containers it´s quite agile and effective to compare those software last versions with several libraries as the runtime can be isolated easily and doesn´t depend on a operating system. So to summarize you can have quite quick several pods with containers ready to test two or three versions of your products with their libraries and plugins, packet managers or several artifacts depending on the version and test features, UX, bugs or just performance.. All aligned with your preferred repository solution: Bitbucket, Git, Github, etc.
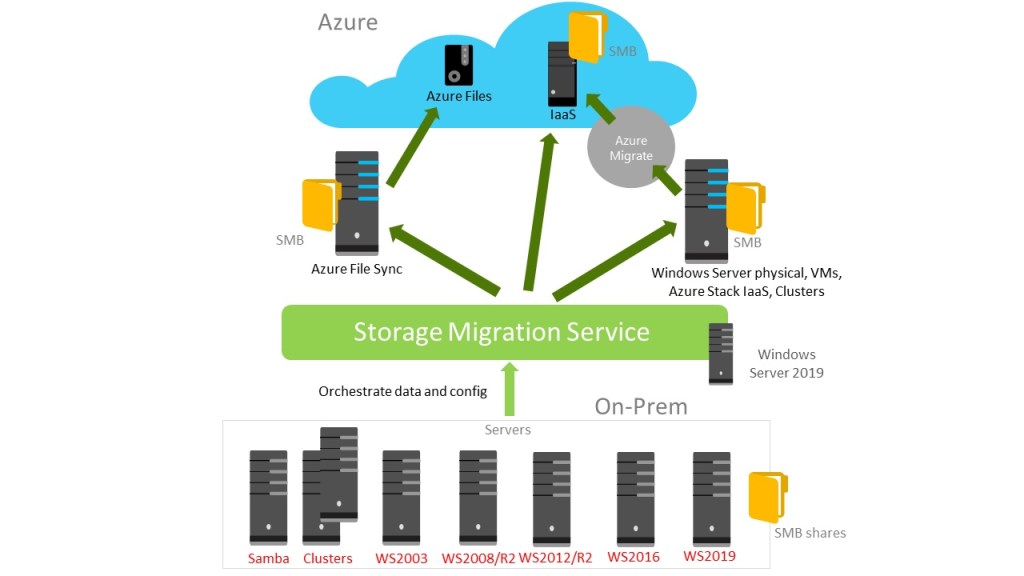
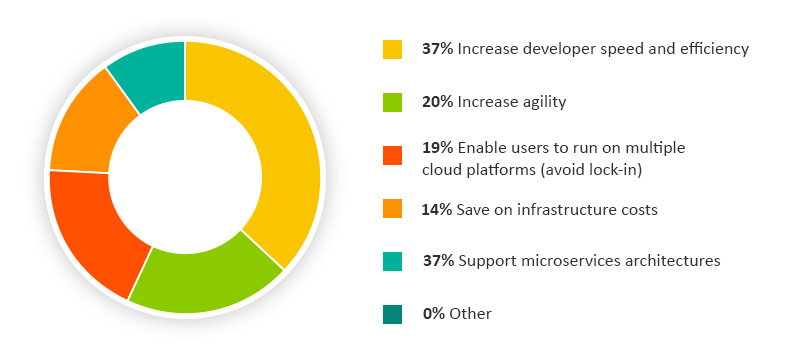
Multicloud – Another fact and quite solid, it´s Kubernetes run on any cloud, private or public and you can orchestrate clusters with nodes wherever you want, without limitations on storage, compute or locations. Even you have at your disposal a great number of tools to orchestrate containers, not just Kubernetes but also Docker Swarm. To conclude, you can see bellow Docker as simple container runtime which was a tendency in RightScale 2019 survey. Now ,and that´s how technology change from one day to the next, Docker as an underlying runtime is being deprecated in favor of runtimes that use the Container Runtime Interface (CRI) created for Kubernetes. … Anyway, Docker is still a useful tool for building containers.

Cost Savings -You can roll out Microservices on demand and without investing a euro on hardware if you want a pure cloud solution. Just create your pads or simple containers and kill them when you want. Pay as you go, pure OPEX. That means reduce CAPEX on hardware and licenses and forget amortization.
Remove your Legacy applications on your on pace – Also, on one hand, big companies want to reduce legacy applications as they need to eliminate monolithic applications, which use to be very critical, with old versions software and dependences on hardware and licences and poor performance and scalability. On the other hand, they are compromise more than ever with the “Cloud first” principle for new IT services because they need to be global, reduce cost and improve resiliency and many CIOs know that public cloud bring those advantages from scratch.
Security – Least but not less. Containerization reduce the expose surface of your applications, eliminate any operating system bug, and allow to take control on known library vulnerabilities with your Software Quality team and your CISO. Networking is also an area where you can watch out the bad guys as traffic is flowing in and out of the containers and you can configure with granularity what is allowed and what not. Finally, you can monitorice the whole microservices solution with open source tools, cloud providers integrated tools or more veteran thirty party solutions.
In the next post we will see differences and similarities between AKS and EKS.
Enjoy the journey to the cloud with me…see you then in the next post.